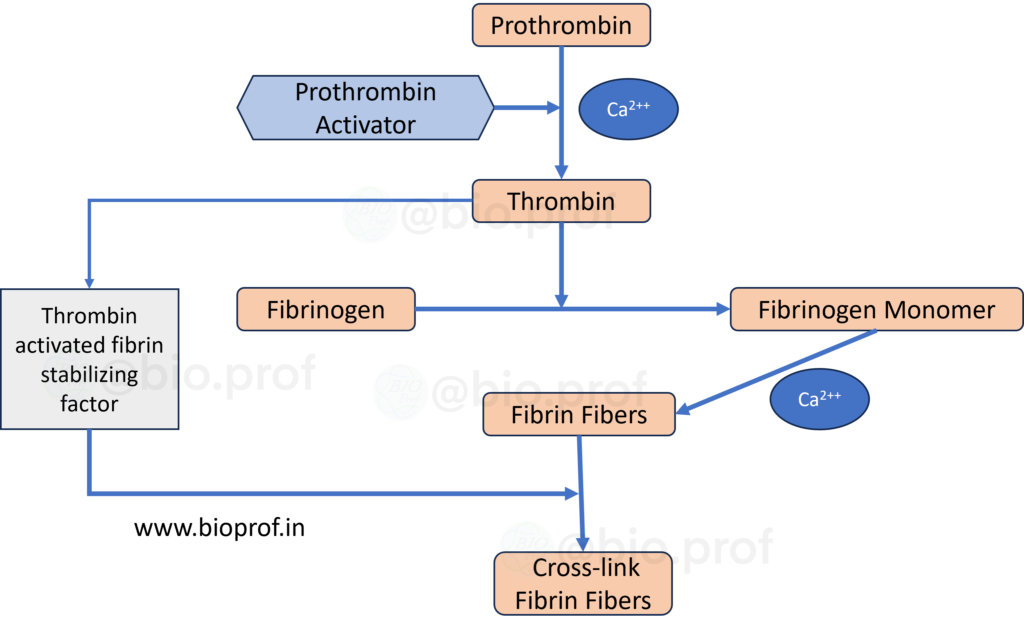
Hemostasis: Formation of a Platelet Plug and Blood clotting
Hemostasis is the body’s natural way of stopping bleeding, and it’s a marvel of our physiological design. It’s most effective in dealing with injuries to small blood vessels like arterioles, capillaries, and venules, which are the usual culprits in everyday bleeding episodes. However, it’s ineffective when controlling bleeding from medium or large arteries.
Hemostasis: Formation of a Platelet Plug and Blood clotting Read More »